Molluscum Contagiosum
Description
Introduction
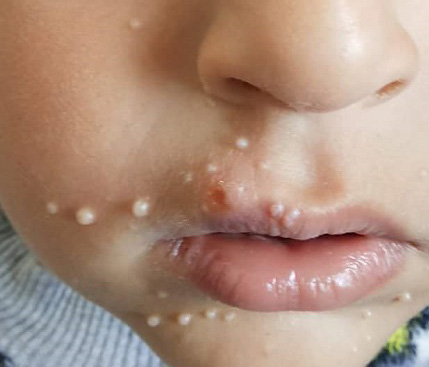
Mollascum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes either single or multiple raised, pearl-like bumps (papules) on the skin. It is a chronic infection, so lesions may persist from a few months to a few years.
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus (the molluscum contagiosum virus) that is part of the pox virus family. The virus is contagious through direct contact and is more common in children. However, the virus also can be spread by sexual contact and can occur in people with compromised immune systems. Molluscum contagiosum can spread on a single individual through scratching and rubbing.
What Are the Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum?
Common locations for the molluscum contagiosum papules are on the face, trunk, and limbs of children and on the genitals, abdomens, and inner thighs of adults. The condition usually results in papules that:
Are generally painless, but can itch
Are small (2 to 5 millimeter diameter)
Have a dimple in the center
Are initially firm, dome-shaped, and flesh-colored
Become softer with time
May turn red and drain over time
Have a central core of white, waxy material
Molluscum contagiosum usually disappears spontaneously over a period of months to years in people who have normal immune systems. In people who have AIDS or other conditions that affect the immune system, the lesions associated with molluscum contagiosum can be extensive and especially chronic.


